Diamond Education
Understanding the 4 C’s of Diamond Shopping
Until 1953, there was no agreed-upon grading system by which diamonds could be judged. GIA (Gemological Institute of America) created the first, and now internationally accepted standard for describing diamonds: Color, Clarity, Cut, and Carat Weight. Now, the 4C’s of Diamond Quality is the universal method for assessing the quality of any diamond, anywhere in the world. The creation of the Diamond 4C’s permits the communication of diamond quality in a universal language so that diamond customers can know exactly what they were about to purchase.

GIA Diamond Reports
A diamond that has a GIA-issued diamond grading report has been examined and graded directly by the GIA. The report contains trusted and highly accurate grading information diamond shoppers can rely on. GIA assesses the diamond’s qualities based on the 4Cs, and documents its grading results. GIA does not certify the diamond’s value. Most of the loose diamonds at Diamond Exchange have an associated GIA grading report.
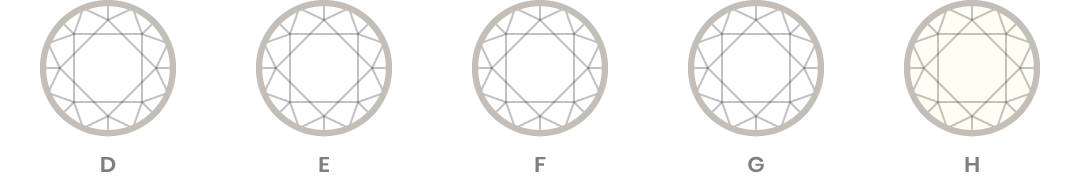
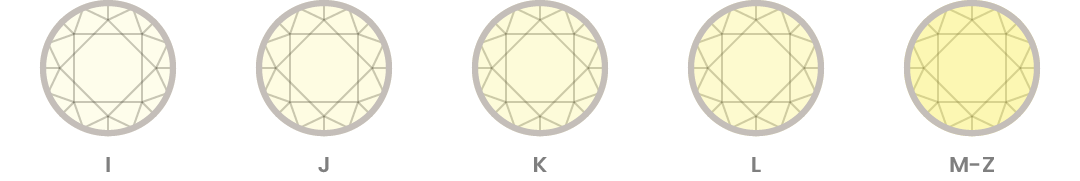
Color
Notably, the diamond color evaluation of gem-quality diamonds is based on the absence or lack of color. The less color a diamond has, the higher its color grade will be. GIA’s D-to-Z diamond color-grading system measures the degree of colorlessness by comparing a stone under controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions to masterstones of established color value. Color variations as subtle and invisible to the untrained eye. For this reason, it is important to get a GIA expert’s color grade for your diamond when evaluating your prospective purchase.
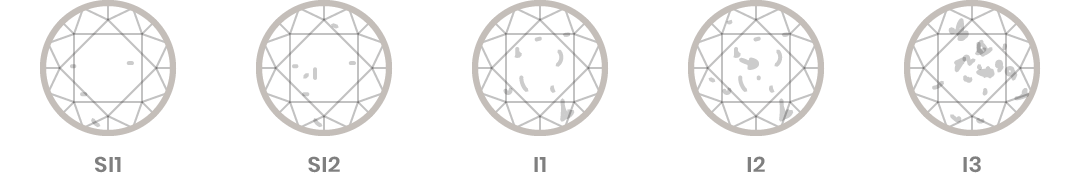
Clarity
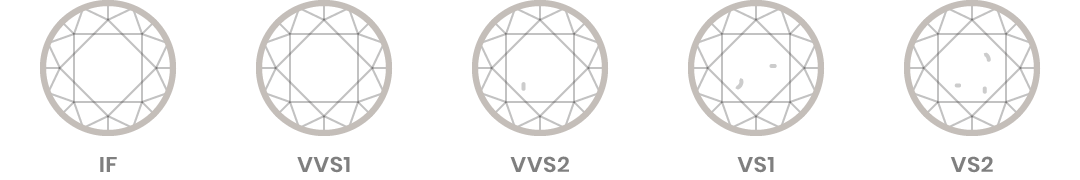
Diamond clarity refers to the lack of blemishes or inclusions in the stone. Remember that no diamond is perfectly pure, but the more pure it is, the better its clarity.
The GIA uses the following grades for diamond clarity:
- Flawless (FL) No inclusions and no blemishes visible under 10x magnification
- Internally Flawless (IF) No inclusions visible under 10x magnification
- Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2) Inclusions so slight they are difficult for a skilled grader to see under 10x magnification
- Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2) Inclusions are observed with effort under 10x magnification, but can be characterized as minor
- Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2) Inclusions are noticeable under 10x magnification
- Included (I1, I2, and I3) Inclusions are obvious under 10x magnification which may affect transparency and brilliance
Because inclusions and blemishes are too tiny to be seen without a microscope, it is very important to have an expert’s assessment of diamond clarity. Clarity is a characteristic that contributes to overall diamond quality and price.
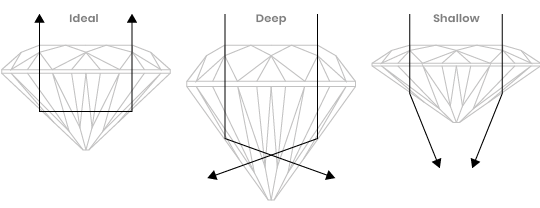
Cut
Diamond cut evaluates the light performance of a diamond and is based on a combination of factors: proportions, symmetry, and polish (the overall surface condition of a diamond’s facets). Cut has the greatest influence on a diamond’s beauty and sparkle. Grading for cut ranges from Excellent to Poor.
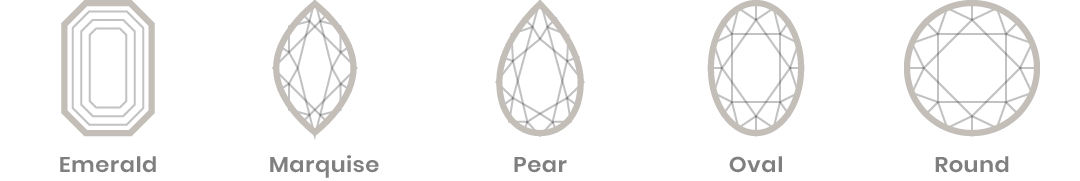
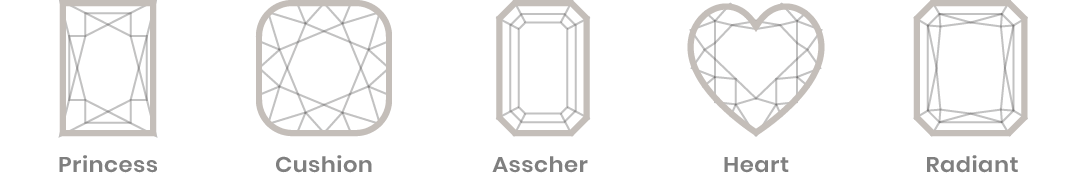
Shape (different from cut)
Often mistakenly termed “diamond cut”, diamond shape is a description of the geometric outline and physical form of a diamond. The shape is an important consideration when buying a diamond since it directly influences price. Because of its sparkle and brilliance, the round diamond is the most popular diamond shape and is generally priced higher than other shapes. The nine common fancy (non-round) shapes for diamonds include princess, emerald, Asscher, cushion, marquise, radiant, oval, pear and heart. Ultimately, the diamond shape that you prefer comes down to personal preference.
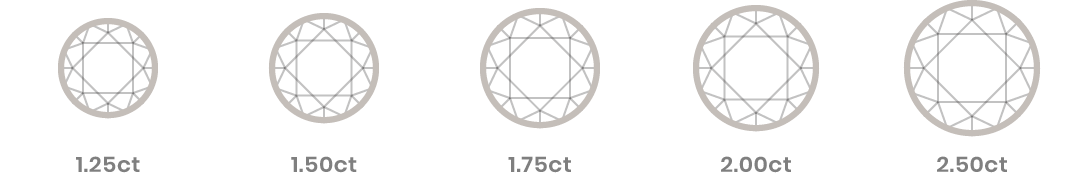
Carat
The carat is a measure of the diamond’s weight, not its size. One diamond carat is equal to 200 mg, or .2 grams, of a diamond. Carats can also be measured in points; 100 points equals a full carat. Carat weight has no bearing on the sparkle of a diamond. Beautiful sparkle is the result of a well-crafted cut. In fact, a high carat weight diamond with a poor cut may look smaller than a diamond with a smaller carat weight and a very good cut.